As AI and machine learning workloads become more complex, developers and enterprises are constantly seeking ways to optimize performance and reduce costs. Traditional GPU usage often leads to underutilized resources, especially when multiple small tasks are assigned to a single, powerful GPU. This is where technologies like Multi-Instance GPU (MIG) and resource scheduling come into play, bringing efficiency, flexibility, and scalability to modern AI infrastructure.
This article explores how MIG and smart resource scheduling can drastically improve system utilization and streamline operations for a wide range of AI applications.
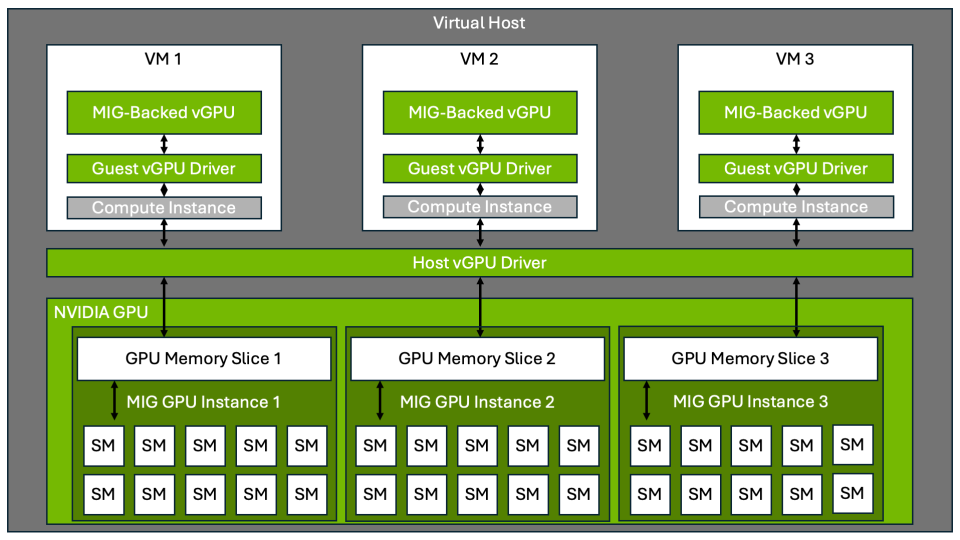
What Is Multi-Instance GPU (MIG)?
Multi-Instance GPU (MIG) is a feature found in newer NVIDIA GPUs that allows a single physical GPU to be partitioned into multiple isolated instances. Each instance operates independently, with its memory, cache, and compute cores. This enables multiple users or processes to run on the same GPU simultaneously without interfering with each other.
Instead of dedicating an entire high-performance GPU to a single task, MIG lets you divide that power across several smaller workloads, maximizing output while minimizing idle time.
Key Benefits of MIG
1. Enhanced Resource Utilization
MIG ensures that every portion of the GPU is used efficiently. By slicing a GPU into smaller units, it allows more tasks to run in parallel, especially for inference workloads or lighter training jobs that do not require the full capabilities of a large GPU.
2. Isolation and Stability
Each instance is fully isolated from the others, preventing one application from impacting the performance of another. This ensures greater system stability and consistency, which is critical in multi-tenant or shared environments.
3. Scalability
MIG is ideal for teams or businesses needing to scale horizontally. Whether supporting multiple developers or serving various machine learning models simultaneously, MIG supports workload distribution without the need for additional hardware.
Role of Resource Scheduling in Efficiency
MIG becomes even more powerful when paired with intelligent resource scheduling. This process involves dynamically allocating GPU instances based on job priority, resource demand, and workload size.
Here’s how effective scheduling further enhances efficiency:
1. Optimised Job Placement:
Schedulers assign tasks to the most suitable GPU instance, ensuring optimal performance and minimum wait times.
2. Queue Management:
Tasks are organized in a queue and processed based on priority and availability, reducing idle time.
3. Load Balancing:
Workloads are evenly distributed across available MIG instances, preventing overload on any single resource.
4. Cost Reduction:
By matching the right task with the right resource, unnecessary energy and compute usage are avoided, leading to better cost control.
Real-World Use Cases
1. Machine Learning Inference:
Instead of dedicating an entire GPU to a single model, MIG allows you to run multiple inference tasks in parallel.
2. Dev/Test Environments:
Multiple developers can work on different projects simultaneously without needing multiple physical GPUs.
3. Edge Computing:
In environments with limited resources, MIG enables maximum output from minimal hardware.
Conclusion
MIG and smart resource scheduling are transforming how modern GPU infrastructure is utilized. They bring flexibility, improve output, reduce costs, and support greater scalability. Whether you are managing cloud-native AI services, running deep learning pipelines, or deploying inference at scale, these technologies ensure that every bit of GPU power is put to efficient use.





